PRODUCT DESIGN
3 min read
User Empathy (Part 1): the factor to create a "gravitational pull" for digital products

Based on the statistics of 61,000+ SKUs representing more than 12,000 new product launches since 2011, Nielsen Breakthrough Innovation Report reveals: 3 out of 4 products in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods sector (FMCG) witnessed failures within the first year. Successful products often have one thing in common: they use consumer-centric researches to uncover key insights driving demand.
Not only in FMCG industry, customer empathy also plays an important role in designing products, especially digital products. Some brands such as IBM, Apple and Google have applied Design Thinking, starting with "Empathize" in a 5-step process to minimize "guessing" decision when creating products and user experience, as well as the limitation in creativity by best practices drawn from successful products, which have already revealed many defects and are not effective over time.
In digital transformation, more and more businesses move towards a user-centric model, emphasize on seeking insights through user empathy, hence, identify the right problems to solve, propose product solutions meeting user's needs. What is empathy in building digital products? What is the importance and how can the team apply this factor to build the impactful digital products satisfying user?
What is Empathy?
As defined in Britannica Encyclopedia, empathy is "the ability to imagine yourself in someone else's shoes to understand a person's feelings, desires, ideas, and experiences". Paul Ekman, a psychologist from the University of California, classifies a person's empathy ability into 3 levels:
- Cognitive empathy: the ability to understand what a person thinks or how they feels.
- Emotional empathy: the ability to understand a person's moods and feelings through emotional connection.
- Compassionate empathy: not only understanding the feelings and thoughts of a person, but also acting to help or support them
For the product team applying Design Thinking, empathy is more than just understanding and sympathy. More specifically, the product team must actively empathize with users to capture all their problems, expectations, wishes, and views related to the business' products, services and industry. A deep understanding of the target audience’s needs will help build digital products that bring more and more value to users, thereby enhance competitive advantages and customer retention, boost growth for businesses.
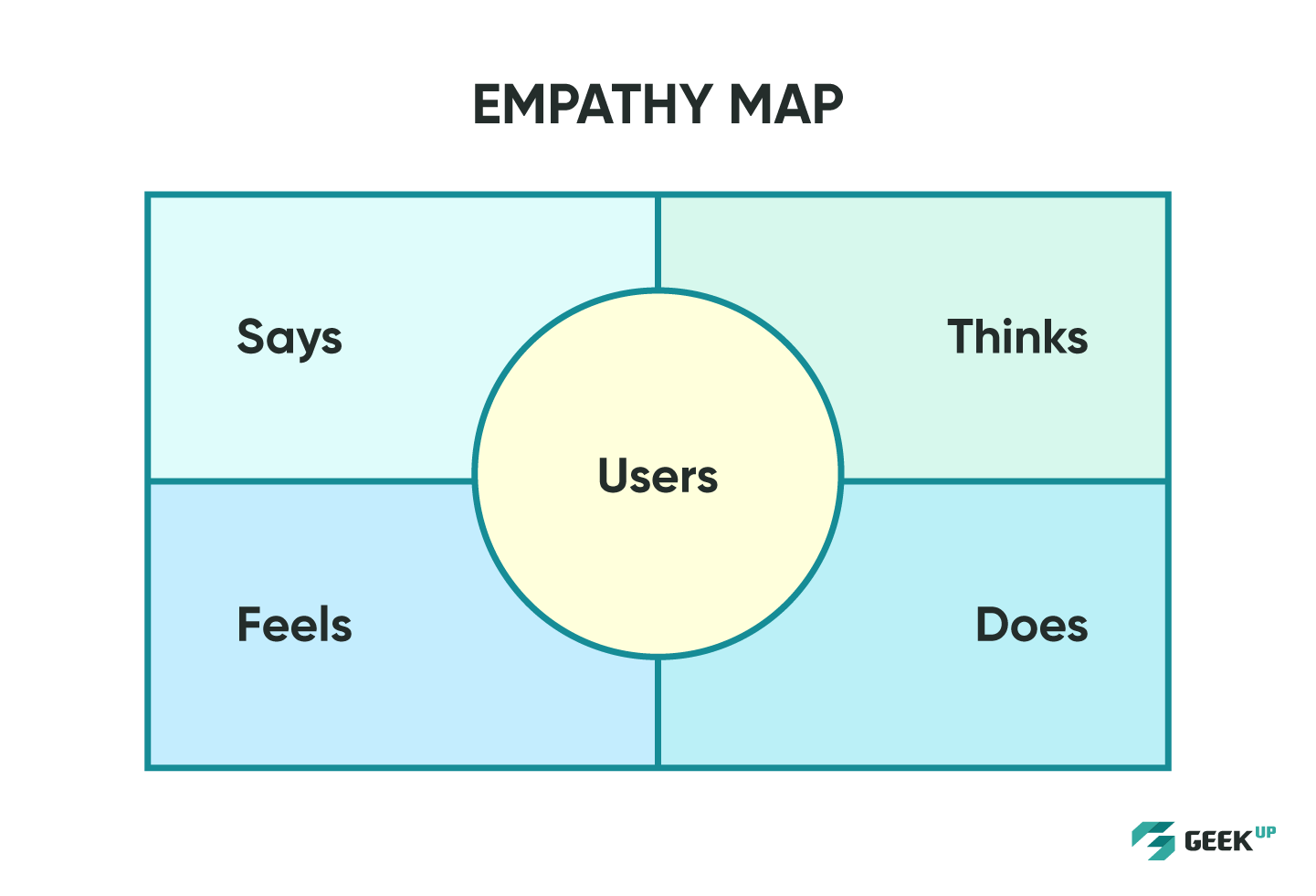
Empathy mapping
Sau khi tiến hành các phương pháp thấu cảm trong quá trình nghiên cứu người dùng, việc tổng hợp các insight và dữ liệu đã thu thập thành một "bản đồ" thấu cảm sẽ giúp đội ngũ làm sản phẩm phác hoạ chân dung về hành vi và cảm xúc của người dùng chính xác hơn cũng như có thể quan sát tổng thể về mọi khía cạnh của người dùng. Để lập bản đồ thấu cảm, đội ngũ thông thường sẽ cần phân bổ các thông tin thu thập được vào 4 mục sau:
After conducting empathy methods during user research, combining insights and data into an empathy map will help the product team get the picture of the user behaviors and emotions more accurately as well as all aspects of the user. In order to do empathy mapping, team need to allocate the information into four categories:
- Says: Original statements shared by users during an interview or usability testing.
- Thinks: Summarizing the user's thoughts during the product experience, especially the thoughts that the user is not willing to share in words. This also helps the product team dig deep into the insights behind that behavior.
- Feels: The emotional state of the user (usually accompanied by a brief sentence describing the context).
- Does: The activities the user will do during product experience or problem solving.
Is user empathy important in digital product design?
Designer Frank Chimero, the author of the famous book "The Shape of Design" once shared: "People ignore design that ignores people." Therefore, a user-centric approach becomes increasingly important. Accordingly, good empathy will help the product team:
- Enhance the ability to propose and come up with more suitable solutions to user needs.
- Lower the failure rate of products due to not fully addressing user needs as well as the context of use.
- Do not underestimate the physical as well as emotional needs of the user.
- Get an overall picture from the insights into how users interact with the world around them.
- Get to know the product's impact on users/customers' lives in research contexts.
- Get insights hidden inside customer's share. Empathic research is more about uncovering motivations and underlying thoughts than facts.
At a broader scale, promoting empathy with users in building digital product in particular and business activities in general will help businesses better serve customers. Businesses will launch products that make a positive impact, not only in line with technological capabilities and business goals, but above all, attracting users with needs have not yet been considered, thereby creating sustainable growth momentum.
User Empathy (part 2): Value methods are indispensable for the product team
References: nngroup.com, marketingweek.com
5 likes
Get latest updates from GEEK Up
Our email packed with digital product insights, trends and case studies.